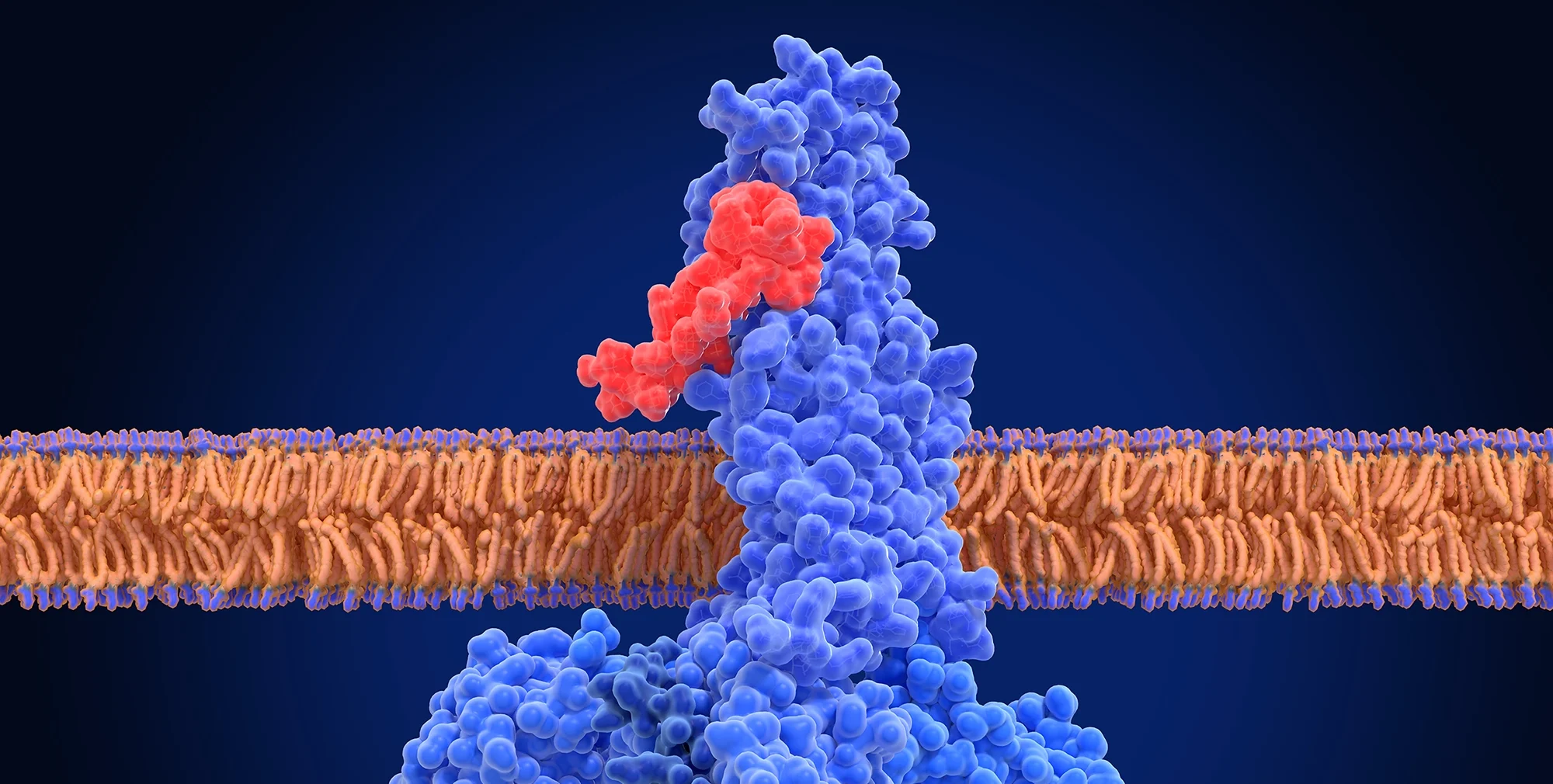
In the context of an integrative approach to treating metabolic and neurological diseases, lifestyle changes and behavioral interventions remain fundamental. However, growing evidence supports the role of certain pharmacological therapies that go beyond their original purpose. Among them, GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) stand out for their ability not only to improve glycemic control and promote weight loss, but also to exert positive effects on the brain. But what exactly are GLP-1 RAs, and why are they generating so much interest in the mental and cognitive health space? Let’s take a closer look.
What Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs)?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications originally developed to treat type 2 diabetes. These drugs mimic the action of an intestinal hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1, which is released after eating. GLP-1 has several effects: it increases insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety. These actions help regulate blood sugar levels and support sustained weight loss.
Beyond Metabolism: Neurocognitive and Emotional Benefits
Beyond their metabolic effects, GLP-1 agonists have been found to cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to receptors in the central nervous system. This means they don’t just act in the pancreas or gut—they also interact with the nervous system, potentially impacting mental and cognitive health. This opens the door to their use in neurodegenerative diseases.
GLP-1 Agonists and Brain Health: What the Research Says
Recent studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs may reduce the accumulation of toxic proteins in the brain, specifically beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. These effects may occur through several mechanisms:
- Enhancing insulin signaling in neurons, supporting their function and survival.
- Reducing chronic neuroinflammation, a significant factor in neurodegeneration.
- Direct activation of brain GLP-1 receptors, promoting neurogenesis and cellular protection (Holscher, 2022).
These mechanisms could translate into real clinical benefits. For instance, the REWIND trial (Cukierman-Yaffe et al., 2020) found that people with type 2 diabetes treated with GLP-1 RAs had a slower rate of cognitive decline than those who weren’t. More recently, preliminary findings presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (2024) showed that patients with mild Alzheimer’s treated with liraglutide experienced slower memory deterioration and up to 50% less volume loss in memory-related brain areas such as the hippocampus.
If confirmed in larger trials, GLP-1 RAs could become revolutionary tools: already-approved diabetes drugs with the added potential to protect the brain and prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
Metabolic Health and Vascular Dementia: An Overlooked Connection
In addition to their direct neuronal effects, GLP-1 RAs offer indirect brain protection by improving vascular risk factors and reducing the likelihood of strokes—thereby lowering the risk of vascular dementia. This dual action makes them particularly valuable for patients with multiple metabolic risk factors.
- Improved metabolic profile: These drugs support weight loss, better glucose control, and balanced blood pressure.
- Reduced cardiovascular risk: They significantly lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes, which can help prevent vascular cognitive decline.
By addressing these systemic issues, GLP-1 RAs help ensure optimal blood flow to the brain, reducing cell damage and improving brain function.
Should GLP-1 Agonists Be Prescribed for Brain Protection?
Currently, GLP-1 RAs are not prescribed solely for cognitive protection in individuals without diabetes. However, patients with metabolic syndrome or diabetes and cognitive concerns may benefit from these drugs. For instance, a middle-aged person with obesity, prediabetes, and a strong family history of Alzheimer’s disease could be an ideal candidate for GLP-1 RA therapy to promote weight loss and metabolic health, with the potential added benefit of neuroprotection.
Conclusion: Bridging Metabolism and Mind
GLP-1 receptor agonists represent one of the most promising tools for connecting metabolic care with brain health. While further research is needed to confirm their preventive or therapeutic use in conditions such as Alzheimer’s, the growing body of evidence suggests that they could play a key role in a truly integrative approach to medicine.
By acting on both the body and the brain, these medications open new possibilities for addressing mental health challenges from a metabolic perspective.
Ready to expand your clinical skills? Advance your expertise with my certification course, Integrative Medicine and Nutrition for Diabetes Type 2, Cognitive Decline, and Alzheimer’s. The course now includes a new 50-page handout update featuring the latest GLP-1 research and evidence-based integrative strategies for your clinical practice. If you’ve already enrolled, this update is available to you at no additional cost.
References
Alzheimer’s Association. (2024, July 30). GLP-1 drug liraglutide may protect against dementia (Press release). Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2024, Philadelphia.
Cukierman-Yaffe, T., Gerstein, H. C., Colhoun, H. M., Diaz, R., García-Pérez, L. E., Lakshmanan, M., Bethel, A., Xavier, D., Probstfield, J., Riddle, M. C., Rydén, L., Atisso, C. M., Hall, S., Rao-Melacini, P., Basile, J., Cushman, W. C., Franek, E., Keltai, M., Lanas, F., Leiter, L. A., … Temelkova-Kurktschiev, T. (2020). Effect of dulaglutide on cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND trial. The Lancet. Neurology, 19(7), 582–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30173-3
Reich, N., & Hölscher, C. (2022). The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: An in-depth review. Frontiers in neuroscience, 16, 970925. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.970925
- Cooking with Spices and Herbs for Mental Health - March 6, 2026
- How Medications Affect Nutritional Status and Why It Matters for Mental Health - February 27, 2026
- Nutrition, Neurodiversity, and Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Integrative Approach to Gut and Brain Health - February 16, 2026

Are You Ready to Advance Your Career?
If you want to advance your career in integrative medicine, explore my courses and certifications.